The life of a dynamic organization
A sociocratic organization can be 3 people small, or ten thousand people large but it always follows the same principles, like a fractal (fractals: a repeating pattern displayed at every scale). That way, it can dynamically grow or shrink as needed. A structural framework for evolution is already present.
Circles in sociocracy will evolve over time. Some organizations start out as full-fledged organizations, some start out as one circle of people working together.
All organizations will go through very similar stages as they differentiate and mature. A sociocratic organizational structure is understood as something that is dynamic, and it is designed to support work getting done. That’s what makes it agile!


Sociocratic Circles
Working circles are the heart of every sociocratic organization. In the working circles, all the day-to-day work of the organization is held and guided.
Authority to those who associate together
Sociocracy translates to “those who associate together govern together”. That presumes that those who perform the work in an organization are the experts in that work and that they have the skills and knowledge to govern their work. No bosses or outside experts are telling them what to do. (Obviously, they will get help and information as they see the need).

Sociocracy translates to “those who associate together govern together”
Power is distributed with the work

As many decisions as possible are made at the most specific level of the organization.
For instance, if a Pastry Circle is linked to a broader Baking circle, the pastry-makers will make as many decisions as possible on their own. If the Pastry Circle wants to change how they make pastry, they do not need the Baking Circle’s approval.
Only decisions that involve the domains of other circles (for instance, shared equipment or spending beyond budget) are made in the broader circles.
We formalize that in two terms:
- Circles in sociocracy have an aim – a description of what it does. That way, we know how all the doings fit together. (Learn more)
- Every circle has a domain – a description of what it can make decisions about. That way, we know who has responsibility and authority over what. (Learn more)
Having this language for distributing authority and responsibility helps us distribute power. Distributed power has many advantages. A system with distributed power will be nimble and resilient, and carry only a small risk of abuse of power. Workers will have a high level of commitment because they are taking full responsibility.
No one will be forced to do anything they see as unnecessary because everyone in the circle will have consented to the policies that govern their work.
Example
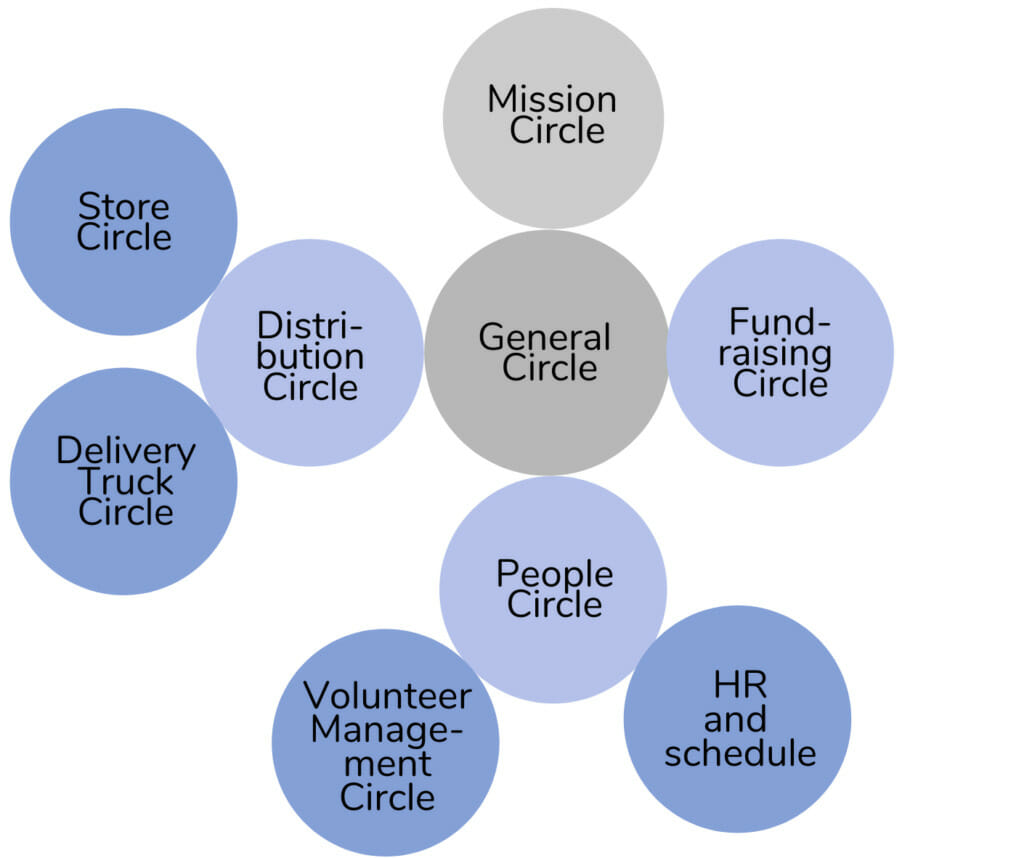
Let’s look at an example. of circles in sociocracy. There are several circles doing work and making decisions – the Store Circle, Delivery Truck Circle, People Circle, Volunteer Management Circle, HR and Schedule Circle and Fundraising Circle.
It’s easiest to imagine that basically all decisions and activities of the organization are done in those circles.
Yet, there is also coordination work and longer-term thinking to do. That’s why there are two special circles:
- The General Circle makes sure that everything fits together. That doesn’t mean it makes many decisions – quite the opposite, they only decide who decides. The General Circle decides about the main circle’s aims and domains, making sure everything has a place where it can be decided.
- The Mission Circle is a place for the long view, where we can discuss how the organization can stay true to its mission.
Read more
Read more about circle structure in sociocracy in our sociocracy manual Many Voices One Song.

Linking and circular hierarchy in sociocracy
Double linking and flow of information
Circles in sociocracy are connected by at least two people serving in the roles of leader and delegate, a principle called linking. The delegate reports bottom-up and the leader top-down, supporting information flow and coherence.


Both attend both circle meetings as decision-making members, and that has a fascinating effect: neither circle can make a decision that overpowers or harms the other, because the people in linking positions would object to such a decision. While consent among prevents power-over among individuals, the combination of consent and linking prevents power-over among circles.
Circular hierarchy
There is still a hierarchy, in the sense that different layers of circles pay attention to different levels of specificity. It’s more about stratification and focus of attention, and expertise.
Double-linking, applied in a bigger organization, creates a flow of information in all directions. We need this flow of information to make sure everyone and everything works well together. The leaders and delegates also serve as a filter – no one in an organization can (and wants to) hold all the information from all the circles. Only what is relevant is passed on, so we can focus on what’s important.

Don’t get hung up on words!
In talking about circles in sociocracy, we may describe how they are linked to each other. In sociocracy, you will hear terms like higher and lower circles, broader/wider and specific/focused circles, up-circles and down-circles, parent and child circles, super circles, and sub-circles.
Some terms trigger in people the fear that sociocratic organizational structure is a power-over system. There is hierarchy in sociocracy – not in the sense of power-over – but in the specificity of domains. The domain level of the shop floor is very specific, while a Board of Directors /Trustees does work that is very broad in scope.
Almost every way of wording has some advantages and disadvantages.
The internal structure of a circle in sociocracy

All circles need some internal structure to function well. Internal structure in sociocracy in built via roles.
- A circle leader is paying attention to the circle’s operation. What needs to be done, who agreed to do it, and how does all the circle’s work come together?
- The circle facilitator plans and manages the circle’s meetings. The facilitator plans the agenda with input from the leader and the secretary, and guides the members through the agenda items according to sociocratic principles (no one ignored). Leader and the facilitator are separate roles because facilitation and overseeing operations are a separate skill set. (The two roles can be held by two different circle members or by the same individual.)
- The delegate is selected by the circle to represent the circle in the next “higher” circle. This creates a double link between two circles (see below).
- The secretary takes notes during the meeting, makes sure the minutes are accessible to everyone in the organization, and maintains the circle’s records. Bigger organizations will choose to have a logbook keeper who keeps the records and the current policies in one central place so they can be accessible.
- Operational roles (in green) are clustered accountabilities as part of the work. For example, machine maintenance might be in the domain of a circle. That circle may then assign responsibility for copy machine maintenance to one member and furnace maintenance to another member. This supports effectiveness because we do not need to involve every circle member in decisions about routine tasks or operations about which they have little information. Ideally, separating out some areas of responsibility will give the circle some peace of mind and reduce the workload in meetings.
A circle will define as many operational roles as they see fit. - Every person can hold more than one role, within a circle and across several circles. Some statistics say that the average person in an organization holds about 7 roles overall.
If you are interested in drawing your own circle structure, this article walks you through the process.
Examples of sociocratic circles
The following structures are snapshots of organizations. The intention is to show you the variety of structures.


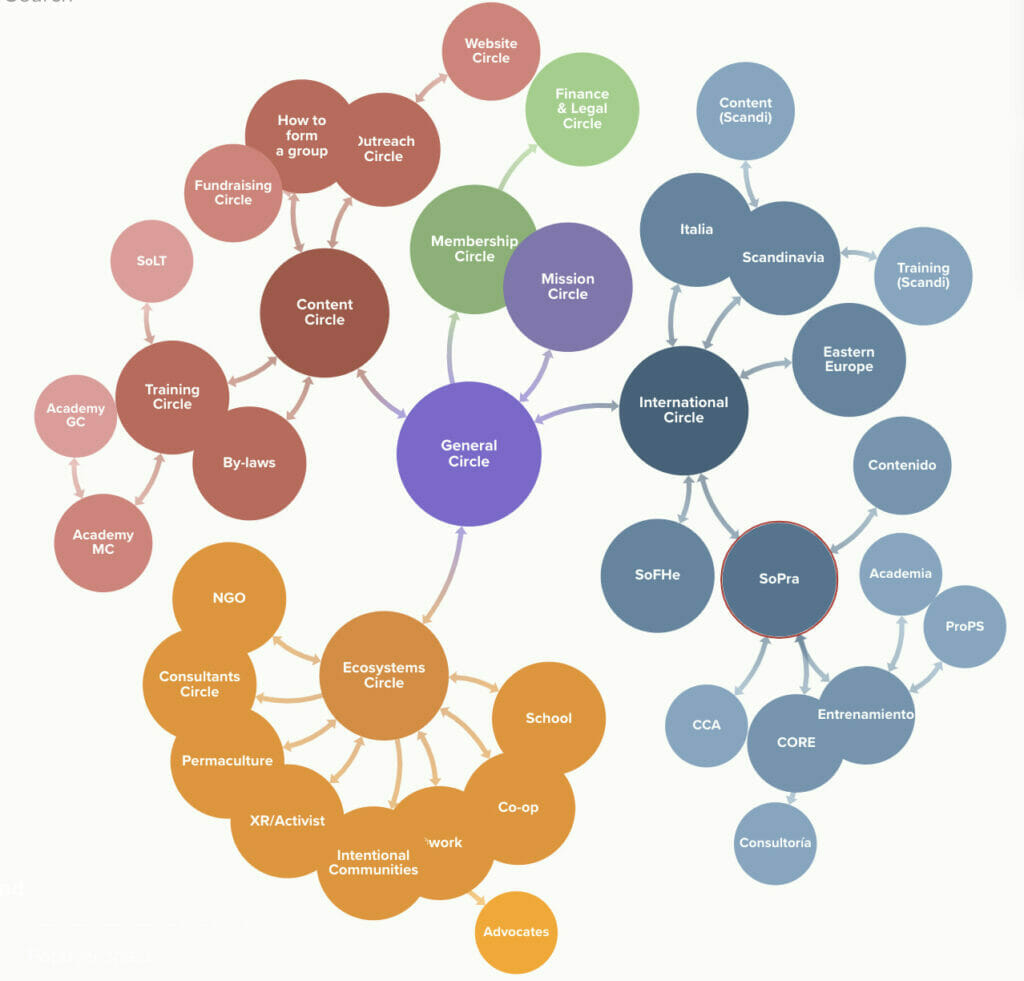

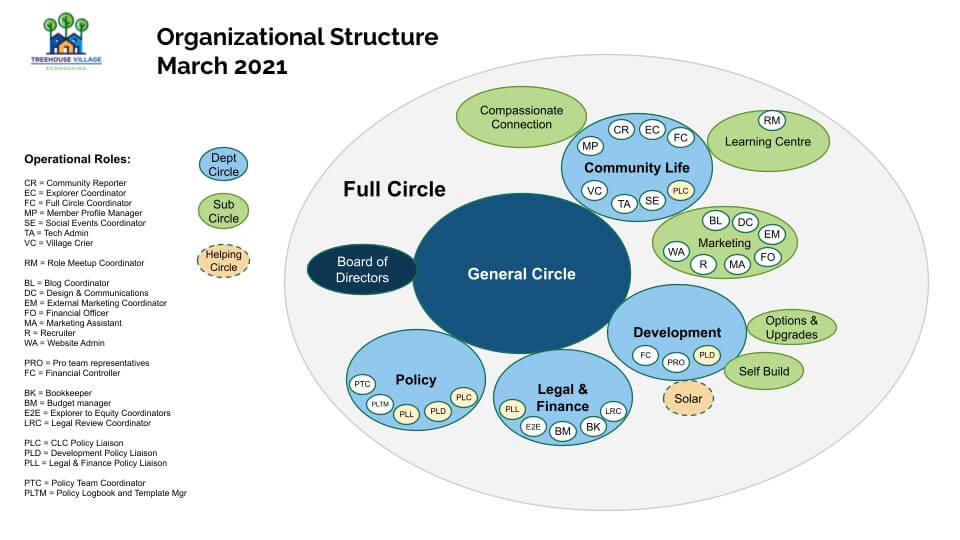




There’s a book about sociocracy!
Read more about circles in sociocracy in our sociocracy manual Many Voices One Song. It’s our reference book for all of sociocracy.

Take our free sociocracy overview class
On-demand video course (~70min) on consent, circle structure, meetings.




