Language: Español
Sociocracy combines consent decision-making, a decentralized system of authority and intentional processes to improve our decisions and processes over time into a governance system that supports effective and efficient process while increasing connection, listening and co-creation among members.
Sociocracy is used in businesses, communities, nonprofits, cooperatives, grassroots groups and in education. See the sociocracy resources on this page to get started.
Go one step deeper:
Free ebook
Are you more the sit-down-and-read type to read all in one go?
We got you!
Download the free ebook and learn more!

Monthly free info sessions
Are you more the “I want to talk to a real human being” kind of learner?
Our free info sessions give you an overview within 60min.
Also ask your questions there.

Books from Sociocracy for All

Many Voices One Song
The practical sociocracy handbook written by the co-founders of Sociocracy For All. 300 pages full of real-life support!

Let’s Decide Together
The definitive guidebook for practicing sociocracy with children. Children can decide with sociocracy too!
Sociocracy topics
Each of these short summaries gives you an overview of the sociocracy resources for you to learn more.
More: Selection process | Writing proposals | Implementation
Making group decisions: consent
Consent is the default decision-making method in sociocracy. In consent, a decision is made when no circle member has an objection. Every person will consent if they can accept the proposal, and object if the proposal has negative implications with respect to the circle’s shared aim.
A group moves to consent in the consent process: presenting the proposal and clarifying questions, quick reactions and a round of consent/objections.
Different from blocking a proposal in consensus decision-making, objections are welcomed as valuable information and they can be integrated by modifying the proposal, its term or its measurements.
Circles and roles: who decides what?
Decisions are made in circles, a defined team of people working together towards their circle’s aim. Circle members make collective policy decisions in their domain and they define operational roles to empower individuals to take on responsibility and circle roles to self-manage their circle.
Circles are connected through parent circle/sub-circle relationships of nested domains, leading to a system where everything can be decided locally in the system, without centralizing power at the center. To make sure two circles are connected, we double-link them with two people as members in both circles.
Sociocracy resources on structure: Overview article on structure
Meetings with sociocracy
Sociocratic meetings are inclusive and efficient with a clear format:
- Opening: check-in and ADMIN
- Content of the meeting
- Consent to agenda
- Agenda items
- Review
- Check-out (meeting evaluation)
Facilitation is a focus of sociocracy. Rounds – the practice of speaking one by one – are commonly used in meetings to keep equivalence and focus. Rounds also make it easy to run virtual meetings in video calls.
Performance
All sociocratic processes are built on the basic idea of continuous improvement. Feedback is a way to improve what we do, both by creating feedback-rich organizations, a commitment to interpersonal feedback and formal, peer-oriented performance reviews. Other practices are: meeting evaluations in meetings, reviews for all policy decisions and for role selections.
Leadership in sociocracy is peer-oriented and based on accountability to own commitments and to the circle. Many people also combine sociocracy with restorative justice or Nonviolent Communication to align their practice with their values and to improve their effectiveness and communication.
Selection process
A sociocratic circle chooses together who will fill an operational or circle role. The most common process to choose that person is the selection process with nominations, change round and consent.
Ready to learn?
More sociocracy resources: articles and videos
-
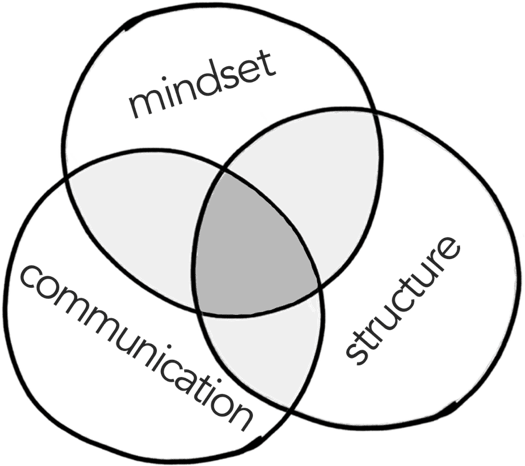
You only need _________ to fix how organizations are run
What do new organizations need? Better structure, better mindset, better communication?
-

Programs for schools: Mindfulness First.
Mindfulness first is a nonprofit that promotes mindfulness in schools and beyond.
-

Breaking Out of the Nonprofit Industrial Complex
Sociocracy is an alternative form of governance in non-profits that supports broad participation and equity in decision-making.
-

Hart’s Mill: Ecovillage and Farm sociocracy case study
Language: Español [et_pb_section fb_built=”1″ admin_label=”section” _builder_version=”3.22.3″][et_pb_row admin_label=”row” _builder_version=”3.25″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat”][et_pb_column type=”4_4″ _builder_version=”3.25″ custom_padding=”|||” custom_padding__hover=”|||”][et_pb_text admin_label=”Text” _builder_version=”3.25.1″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat”] Hart’s Mill Ecovillage and Farm is becoming a reality, and […]
-

There is no hierarchy in sociocracy…right?
Language: Español “Is there hierarchy in sociocracy?” is a fairly common question. And since people expect me to say no, I always say yes. Why? Because that’s the best way […]
-

The tragedy of the meeting: Meeting time as an example of a common pool resource
Meeting time is lifetime shared with others. How do we share these resources well? This article highlights Prosocial’s Core Design Principles with the example of meeting time as a common pool resource and shows how tools from sociocracy help share time in a collaborative way.
-

Circles in sociocracy: an effective organizational structure
Circle structure in sociocracy: nested circles, linking, helping circles and special circles.
-

Sociocracy and NVC at a Dutch Democratic School
Cordelia Addison
-

For purpose: Galgael
A social enterprise giving people more opportunity.
-

Clarity and empowerment: What is a domain?
Language: Español Domains in sociocracy – while they are innocent-looking, they are the foundation that makes sociocracy so transformative – with empowerment, and clarity! So what are domains? Each circle […]
-

Let’s Decide Together! Book Launch
Language: Español Let’s Decide Together! is an accessible workbook for anyone interested in practicing sociocracy with children. Readers can use this book to make more values-aligned, egalitarian, and inclusive decisions […]
-

How sociocracy promotes vulnerability, trust, and psychological safety
A summary of research into psychological safety and shared leadership, and how sociocracy may promote benefits of psychological safety in the workplace.